Skill gaps, where employees lack the competencies needed to fulfill their roles effectively, represent a silent but significant cost for organizations. While the issue is often discussed in the context of employee training or recruitment, its broader financial and operational implications remain largely underestimated.
A Study from McKinsey in 2023 estimates that skill gaps can lead to 20%-25% lower productivity in roles affected by digital transformation.
In today’s fast-paced business landscape, staying competitive requires more than just innovative products or aggressive marketing. One of the most critical and yet frequently overlooked elements of long-term success is the workforce’s capability to perform at the level required by the company’s strategy.
We look in this article at the hidden costs of skill gaps for companies.
What is a Skill Gap?
A skill gap occurs when there’s a discrepancy between the skills an employee possesses and the skills required for their job. This gap can stem from various factors: rapid technological change, shifts in job roles, poor onboarding, or even misaligned hiring practices.
These gaps are not always easy to detect. Sometimes they manifest subtly — through decreased productivity, rising error rates, or customer dissatisfaction. Other times they’re more visible, such as through missed deadlines or the inability to adapt to new systems. Regardless of how they appear, their impact can ripple across an entire organization.
The Hidden Costs of Skill Gaps
From Hiring to higher Turnover, Skill Gaps have a huge impact on Companies. While it varies by company size, industry, and role, skill gaps can cost a mid-sized company $1M+ per year. Let’s go deeper into the estimated costs.
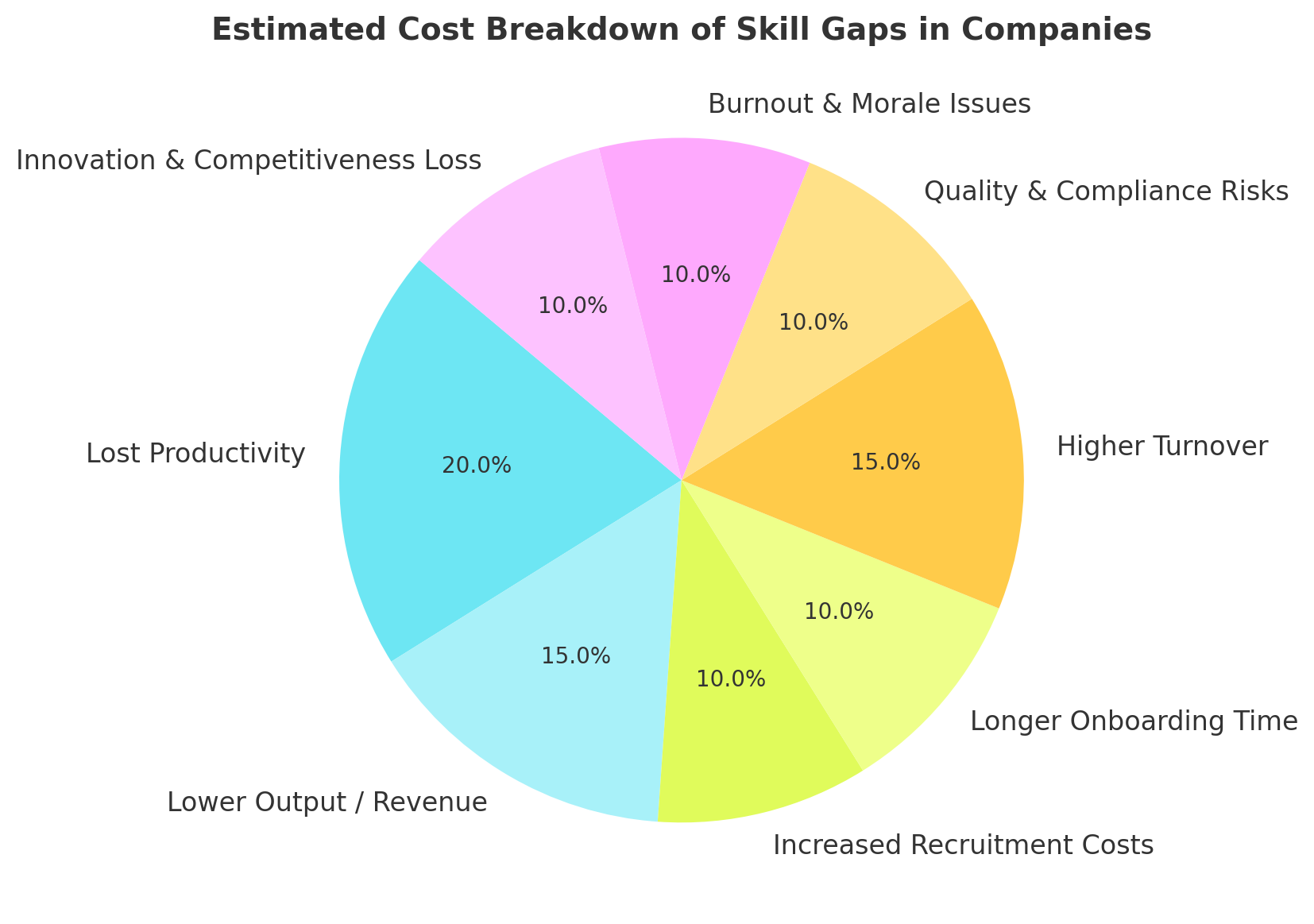
1. Decreased Productivity
When employees don’t have the right skills, tasks take longer to complete, and the quality of work may decline. This inefficiency compounds over time, reducing the overall productivity of teams and departments. What might look like an issue of laziness or disengagement is often simply a matter of lacking the proper tools — in this case, skills — to perform well.
2. Increased Operational Errors
Employees operating without adequate knowledge or skill are more prone to making mistakes. In industries like healthcare, finance, or manufacturing, such errors can be costly — not only financially but also in terms of compliance, safety, and reputation.
3. Lower Employee Engagement
Skill gaps don’t just affect output — they also take a toll on employee morale. Workers who feel ill-equipped to do their jobs often become frustrated, disengaged, or anxious. Over time, this can result in burnout, absenteeism, or increased turnover — all of which come with their own associated costs.
4. Higher Recruitment and Training Expenses
Many companies attempt to resolve skill gaps by hiring new talent. However, recruitment is expensive. According to various industry studies, replacing an employee can cost between 30% to 150% of their annual salary. Moreover, if the organization lacks a structured upskilling strategy, the new hire may face the same gaps within months, leading to a repetitive and costly cycle.
5. Lost Revenue Opportunities
Skill gaps can slow down the adoption of new technologies, delay product launches, and hinder innovation. In competitive markets, this lag time can lead to lost revenue opportunities. For example, if a sales team lacks the digital skills needed to leverage CRM tools effectively, they may underperform despite having a quality product.
Why Skill Gaps Are Often Underestimated
1. Lack of Visibility
Unlike hard costs that show up in financial reports, skill gaps are intangible. They’re not itemized on balance sheets or invoices, so they often go unnoticed until they result in something more tangible — like a failed project or missed KPI.
2. Focus on Short-Term Metrics
Many organizations prioritize short-term outcomes: quarterly profits, monthly targets, or daily task completions. As a result, they may neglect the deeper, systemic issues affecting performance, like inadequate skills or mismatched job roles.
3. Misalignment Between HR and Business Strategy
Often, HR departments operate in isolation from business units. Without a close alignment to strategic goals, HR might not fully understand where skill gaps are emerging or how critical they are. This disconnect limits proactive responses.
4. Underinvestment in Learning & Development (L&D)
Some companies treat training as a one-off event instead of an ongoing process. Budget constraints and skepticism about ROI contribute to underinvestment in L&D, despite overwhelming evidence that structured development programs improve retention, productivity, and agility.
Closing the Skill Gaps: A Strategic Approach
1. Conduct Skills Audits
Regularly assess the current skills of your workforce against the skills needed now and in the near future. This can be done with a Skill Management Software like Teammeter which combines self-assessments with 360° Feedback. In a previous article, we explained how to make a skill gap analysis with Teammeter.
2. Align Skills Development with Business Strategy
Skill-building should not occur in a vacuum. Tie learning objectives to strategic goals like market expansion, digital transformation, or customer experience improvements.
In Teammeter, you can define goals for workforce planning that align to your strategic goals.
3. Personalize Learning Pathways
Avoid generic training programs. Instead, use data to tailor learning experiences to individual roles and career aspirations. This builds needed competencies and increases employee engagement.
In Teammeter each Employee has a development plan with training courses suggested by AI.
4. Leverage Technology
Use platforms that allow for adaptive learning, microlearning, and on-the-job performance support. Modern learning management systems (LMS).
5. Encourage a Culture of Continuous Learning
Leaders must model curiosity and development. Encourage employees to see learning as a core part of their job rather than a periodic obligation. Celebrate growth and reward initiative.
6. Measuring the Impact
Quantifying the financial impact of skill gaps is complex, but essential. Here are a few methods:
- Performance Metrics: Compare team outputs before and after training interventions.
- Error Rates: Track the frequency and cost of operational errors tied to specific skill deficits.
- Turnover and Absenteeism: Analyze exit interviews and absentee records for mentions of inadequate support or training.
- Customer Feedback: Monitor complaints and satisfaction scores related to service quality.
Using such data, companies can estimate the ROI of closing skill gaps and make a stronger case for L&D investment.
A Competitive Imperative
In an era of digital disruption, remote work, and rapid innovation, the ability to learn and adapt is as critical as technical expertise. Organizations that fail to address skill gaps risk stagnation, higher costs, and missed opportunities.
On the other hand, those that treat workforce capability as a strategic asset will gain a sustainable competitive edge. By identifying, measuring, and addressing skill gaps proactively, companies can reduce hidden costs, increase resilience, and unlock their full potential.
Sources
- World Economic Forum (WEF) – Future or Jobs Report 2023
- McKinsey & Company – Rethink reskilling for the post-pandemic world
- Grant Thornton (UK) – The skills gap and its impact on productivity
- ScienceDirect – Understanding and measuring skill gaps in Industry 4.0

